Table of Contents
IP Multicast
General
- Multicast is a layer-3 (IP) feature (Multicast Routing).
- Multicast Switching is a complementary technology at layer-2
this is generally called: “IGMP snooping”
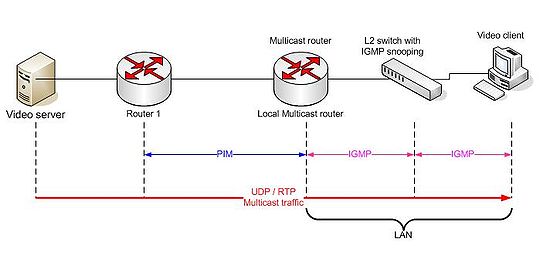
IGMP Snooping
Essentially, IGMP snooping is a layer 2 optimization for the layer 3 IGMP protocol. IGMP snooping takes place internally on switches and is not a protocol feature.
- IGMP is doing the same thing in IPv4 as “Multicast Listener Discovery” (MLD) in ICMPv6
- Active IGMP Snooping = “IGMP proxy” = RFC 4541
“Considerations for Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) and Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) Snooping Switches” - the Generic Attribute Registration Protocol (GARP) protocol was used by the application “GARP Multicast Registration Protocol” (GMRP). Today most switches prefer IGMP-Snooping over GMRP.
IP multicast addressing
IP Multicast addresses are Class D subnet (first bits: 1110): 224.0.0.0/4 (224.0.0.0-239.255.255.255) with reserved: 224.0.0.0/24 network control traffic (routing protocols like OSPF) 224.0.0.1 all-hosts = all systems on subnet 224.0.0.2 all-routers = all multicast routers on a subnet 224.0.0.5 OSPF All Routers 224.0.0.6 OSPF Designated Routers 224.0.0.9 RIP2 224.0.1.1 NTP 224.0.1.0/24 Internetwork Control Block (RSVP, DHCP) 224.1.0.0/16 ST Multicast Groups 224.2.0.0/16 SDP/SAP Block 239.0.0.0/24 reserved for boundaries
IP to MAC mapping
According to IPv4 multicast standards, the MAC destination multicast address begins with 01:00:5e and is appended by the last 23 bits of the IP address. 01:00:5e:00:00:00-01:00:5e:7f:ff:ff 224.128.64.32 -> 01:00:5e:00:40:20
MBONE
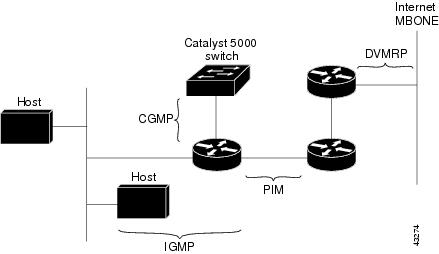
IGMP
PIM
- wikipedia → Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM)
DVMRP
Novell Imaging over Multicast
The name of the multicast session. Each workstation joining the session uses the same value for this parameter. NOTE: The name must be unique among concurrent multicast sessions. It is hashed by the imaging engine to produce a Class D IP address for the multicast session. To facilitate troubleshooting (wire sniffing), all Desktop Management Workstation Imaging multicast addresses start with 231. For example, the session name doug produces the multicast address 231.139.79.72.
Reliable Multicast
- RML = Reliable Multicast Library → http://www.land.ufrj.br/tools/rmcast/rmcast.html
Cisco
- IP Multicast support page
- Cisco TechBrief: Internet Protocol IP Multicast Technology
- Cisco Group Management Protocol (CGMP)